Want to code faster? Our Python Code Generator lets you create Python scripts with just a few clicks. Try it now!
In this tutorial, we will make a simple text adventure game with Python and some of its modules like os, json, and pyinputplus.
We will focus on the code and make a system that allows prompts that lead to many other prompts. We also make an inventory system.
Let us go over how the text adventure story will be stored. Below you see a template of one prompt:
"0": ["Text", [possiblities], "My Text", "action"],Each prompt will be an item in a dictionary that contains a list of four items. We use a dictionary because there can't be any duplicate keys. The first item of the list will be the text of the prompt itself, and the second one is another list that holds the indexes/keys of the prompts this one can lead to.
The third item is the text of this prompt when used on other prompts. When we program the system, we will see what this means, and last but not least, we have the action of this prompt. This will tell the program whether to add or subtract a kind of item.
Below is our (really pointless) story. As you see, the first prompt leads to prompts one and two, and so on.
{
"0": ["You embark on a new adventure, you are at a conjunction where do you go?", [1, 2], "Go Back", ""],
"1": ["You Encounter an angry Mob of Programmers, what do you do?", [3, 4], "Go Right", ""],
"2": ["You see the City of schaffhausen in front of you", [0, 3], "Go Left", ""],
"3": ["I dont know why you did that but okay.", [4, 5], "Use Banana", "minus-clock"],
"4": ["Seems like it worked they did not notice you. One of them slips you a banana", [4, 5], "Pull out Laptop", "plus-banana"],
"5": ["The Banana was poisonous", ["end"], "Eat Banana", ""],
"10": ["You fell over and now you are in grave pain ... ", ["end"], "Pull out Laptop", ""]
}The whole story is saved in a JSON file named story.json. Let us start coding.
Imports
We start with the imports. We get the os module to clear the console before every prompt, so the console is cleaner. We also get json to parse the .json file to a valid Python dictionary. Lastly, we get the pyinputplus module to use the inputChoice() function, giving the user a limited number of correct items to choose from. Remember that we have to install it with:
$ pip install PyInputPlus# Import pyinputplus for choice inputs and os to clear the console.
import pyinputplus
import os
import jsonSetting up some variables
Let's continue setting up some variables and opening the .json file. The currentKey variable will hold the key of the current prompt and currentKeys will have all possible following keys/prompts of the current prompt.
The itemAlreadyAdded variable will just be used to tell whether we have already been here or not in the last prompt. This will be used when we want to display the inventory.
# setting up some variables
currentKey = '0'
currentKeys = []
itemAlreadyAdded = FalseAfter that, we will open the JSON file with a context manager and parse the file with json.load(). We store the parsed dictionary in the storyPrompts variable.
# Get the Story Prompts
# A dictionary is used because we dont want to allow
# duplicate keys
with open('story.json', 'r') as f:
storyPrompts = json.load(f)You can check this tutorial to learn more about JSON files in Python.
In the end, we also define a dictionary that holds the inventory.
inventory = {
'banana(s)': 0,
'clock(s)': 2,
'swords(s)': 0,
}StoryPrompts Check
We will now briefly transform the story dictionary to work with our program. To do this, we loop over it and get the prompt text and the leading keys. *_ is used to omit the other values that are to be unpacked.
# Check if the prompts are valid
for prompt in storyPrompts:
promptText, keys, *_ = storyPrompts[prompt]We first will check if the prompt text ends with a ':'. If that is not the case, we add it and set the value in the dictionary.
# Add ":" at the end of the prompt Text
if not promptText.endswith(':'):
storyPrompts[prompt][0] = promptText + ': 'After that, we also transform all the numbers in the leading keys list into strings because we can only access a dictionary with strings, not integers.
# Check if the keys are strings, if not transform them
storyPrompts[prompt][1] = [str(i) for i in keys]Prompts Loop
Before making the prompt loop, we give the user instructions, telling him that he can view the inventory with the -i command.
# Giving the user some instructions.
print('Type in the number of the prompt or -i to view your inventory ... have fun.')Now let us get into the prompt loop. This is an infinite while loop that we will stop from within.
# Prompt Loop
while True:In the loop, we start by clearing the console with the os.system() function.
# Clearing the Console on all platforms
os.system('cls' if os.name == 'nt' else 'clear')After that, we get all the data from the current prompt except its text in other prompts and save them to variables.
# Get the current prompt all its associated data
currentPrompt, currentKeys, _, action = storyPrompts[currentKey]Now, if the string 'end' is in the currentKeys list, we know that this prompt is the end so that we will exit the while loop:
# Finish the Adventure when the next keys list contains the string 'end'
if 'end' in currentKeys:
breakBut in most cases, the loop will continue with the loop, so we know to check if the action says something special. Remember, the action is the last item on the list. If minus or plus is in the action, we know that the action will add or subtract to the items dictionary. Currently, we only do all this if itemAlreadyAdded is False:
# Look for inventory Changes
if not itemAlreadyAdded:
if 'minus' in action:
inventory[action.split('-')[1]+'(s)'] -= 1
if 'plus' in action:
inventory[action.split('-')[1]+'(s)'] += 1Next, we loop over all of the currentKeys to add them to the prompt text, so the user knows their options.
# Add Option Descriptions to the current Prompt with their number
for o in currentKeys:Now the tedious thing about this is that we have to check if the prompt this option leads to subtracting an item that the user did not have. In the code block below, we do just that. We first define a variable and get the action from the option prompt. Then we check if the string minus is in the action. If that is the case, we get the item from the action, which will be after a '-'; that is why we split it by that.
Last but not least, we check if this item is zero, which means this route is not available because it will subtract an item that the user has none of. Then we set invalidOption to True:
invalidOption = False
thisaction = storyPrompts[o][3]
if 'minus' in thisaction:
item = storyPrompts[o][3].split('-')[1]+'(s)'
if inventory[item] == 0:
print(storyPrompts[o][3].split('-')[1]+'(s)')
invalidOption = TrueSo if the option is valid, we add it to the prompt text with the number the user has to type in to get there.
if not invalidOption:
currentPrompt += f'\n{o}. {storyPrompts[o][2]}'After adding all the valid options, we also add a string telling the user what do you do?
currentPrompt += '\n\nWhat do you do? 'Now we can finally ask the user what they do. To do this, we use the pyinputplus.inputChoice() function, which has a choices parameter that we can supply with a list of strings representing the options the input will allow. That is why give it the currentKeys plus the string -i, which the user can use to display the inventory. The prompt argument is our prompt which we build earlier.
We save this input in the userInput variable.
# Get the input from the user, only give them the keys as a choice so they dont
# type in something invalid.
userInput = pyinputplus.inputChoice(choices=(currentKeys + ['-i']), prompt=currentPrompt)Now if -i is in the user input, we know the user wants to see their inventory:
# Printing out the inventory if the user types in -i
if '-i' in userInput:
print(f'\nCurrent Inventory: ')
for i in inventory:
print(f'{i} : {inventory[i]}')
print('\n')
input('Press Enter to continue ... ')We also set the itemAlreadyAdded variable to True, which is just done to ensure that we don't add or subtract an item again later. If the user did not type in -i. we set this same variable to False. In the end, we also set the currentKey to the userInput.
itemAlreadyAdded = True
continue
else:
itemAlreadyAdded = False
currentKey = userInputAfter the loop
After the prompt loop, we print out the text of the last prompt.
# Printing out the last prompt so the user knows what happened to him.
print(storyPrompts[currentKey][0])
print('\nStory Finished ...')Show Case
Now let's see the text adventure in action:
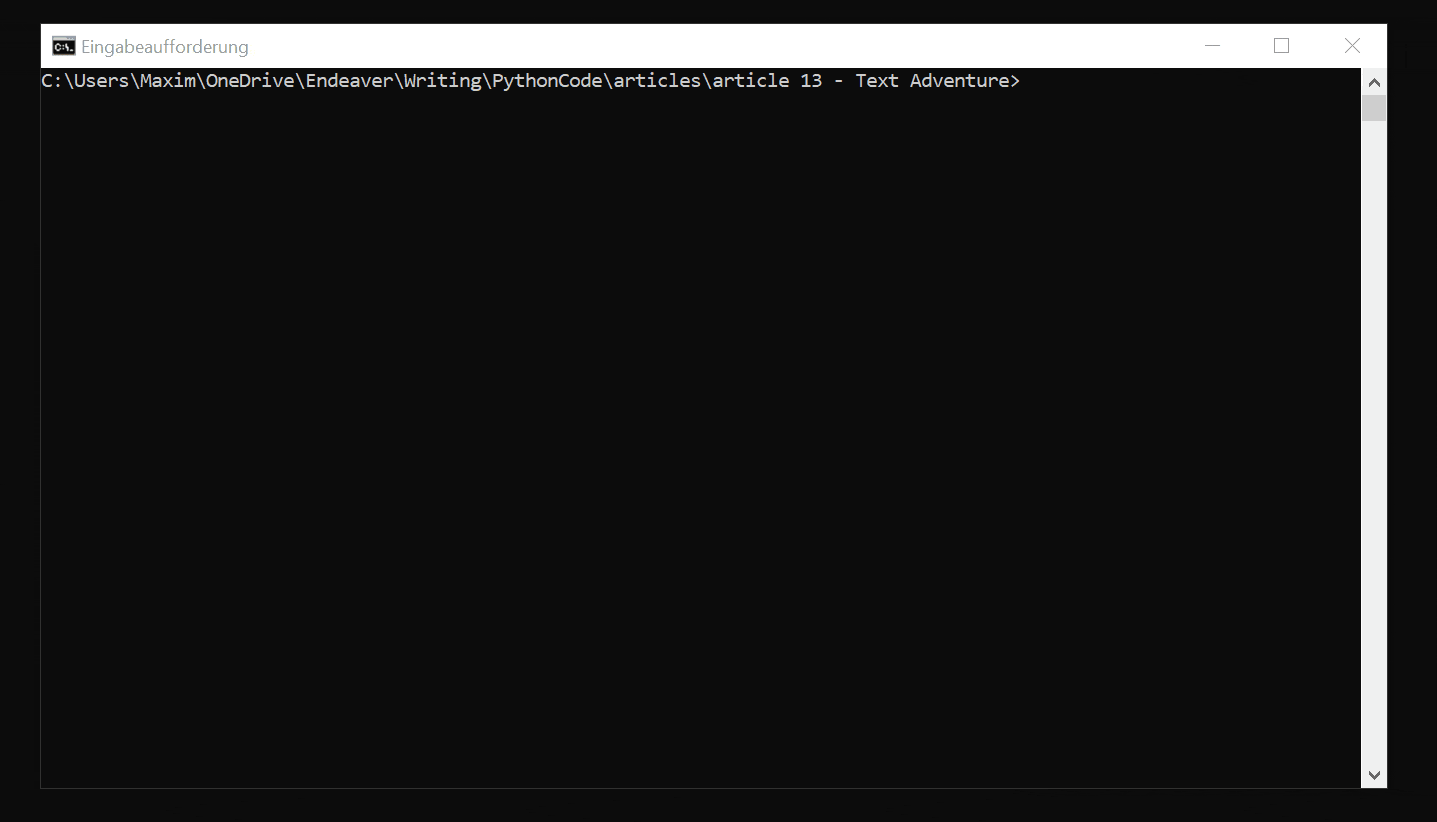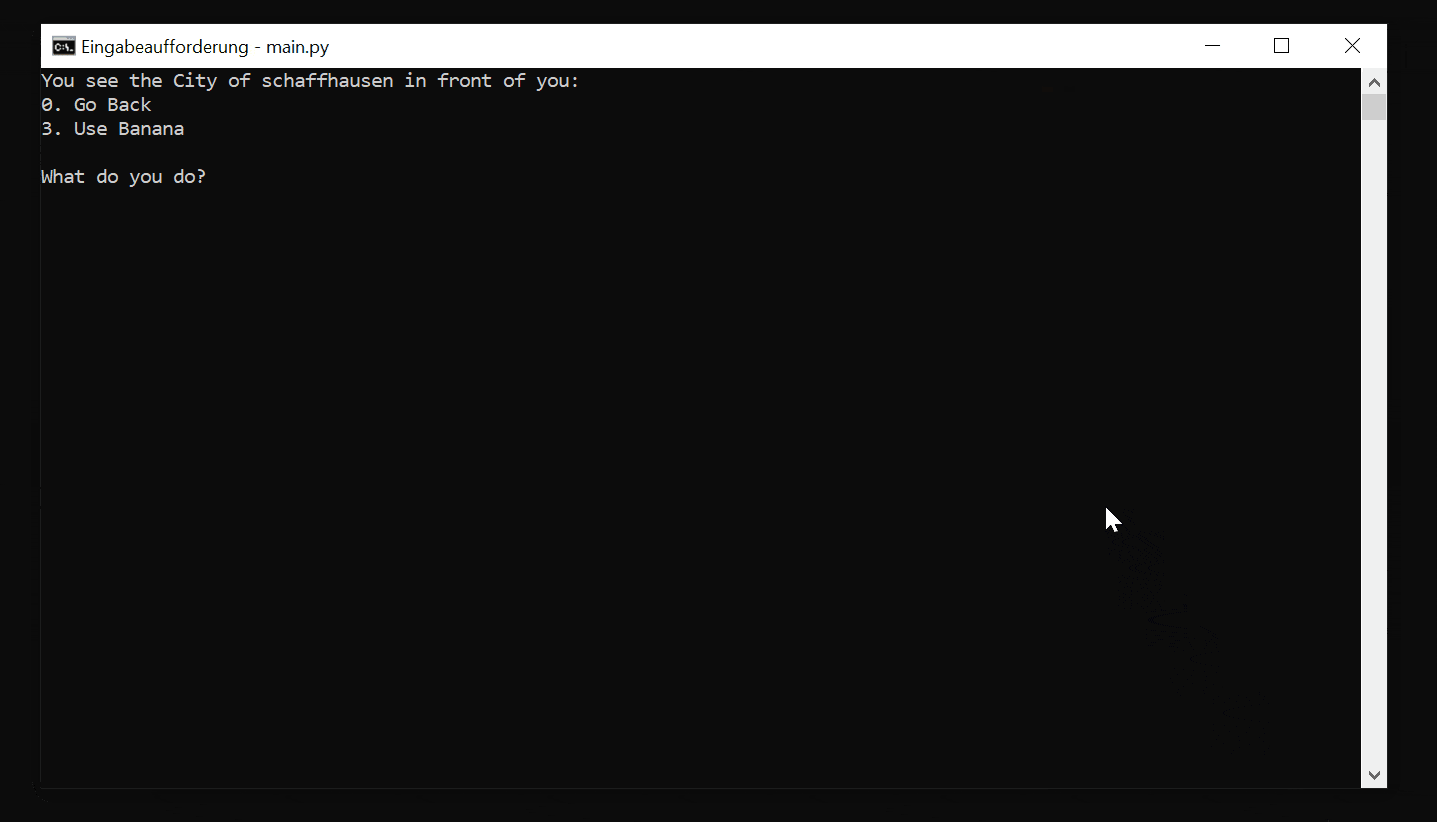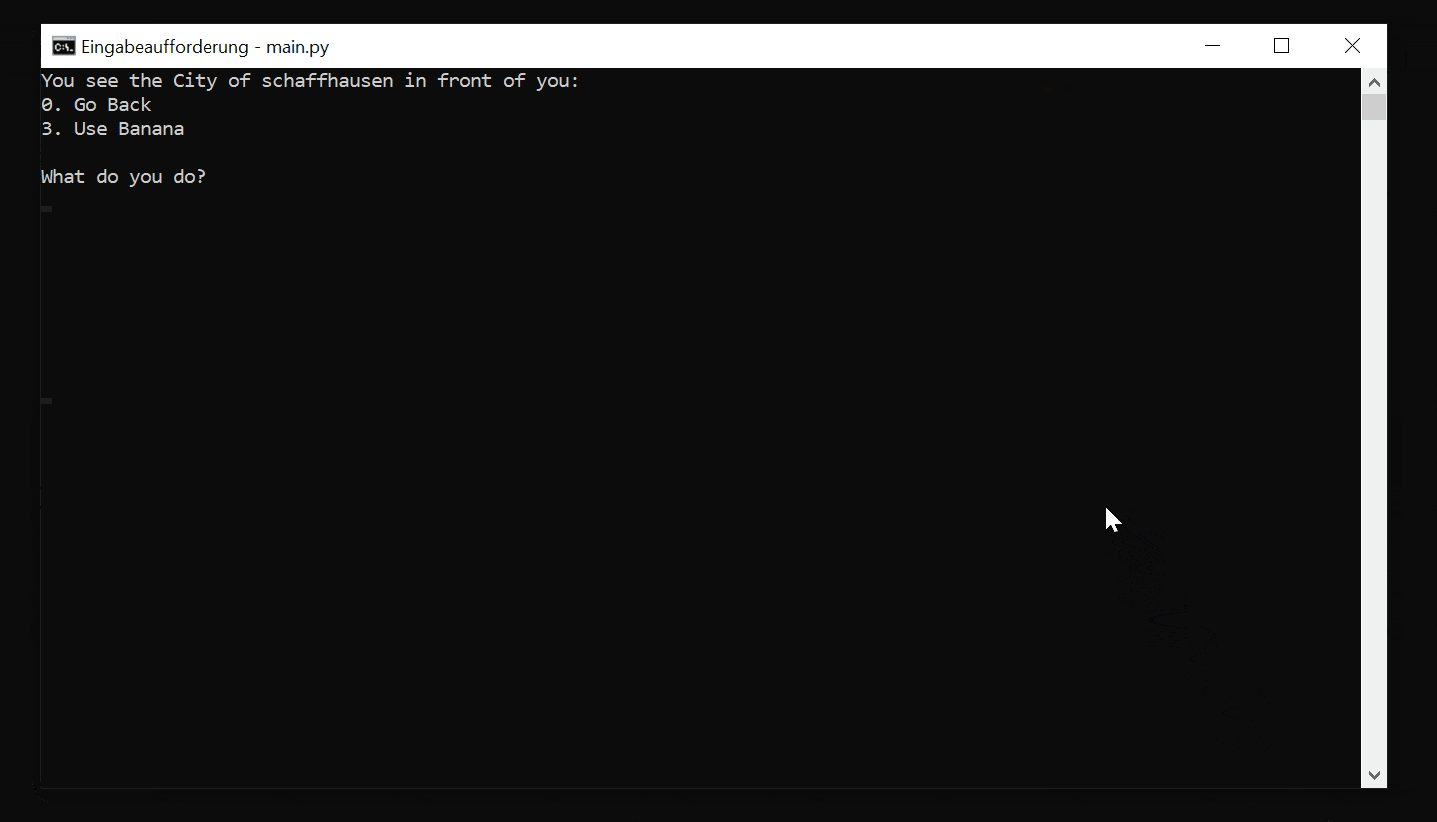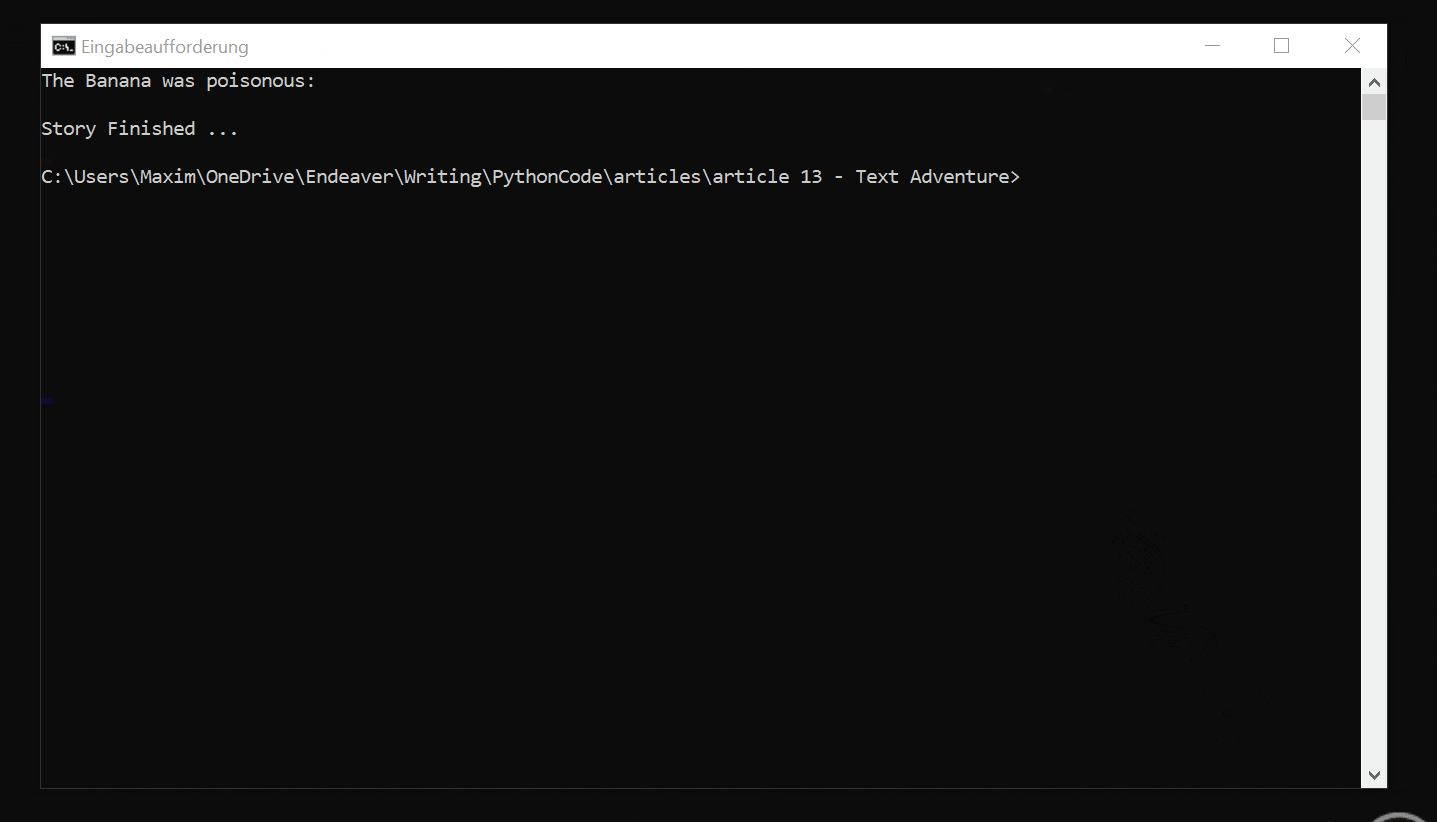
Conclusion
Excellent! You have successfully created a text adventure game using Python code! See how you can add more features to this program, such as more checks for the story prompts or more action types. You can also edit the story.json to make a completely different story without changing the code!
Learn also: How to Make a Simple Math Quiz Game in Python.
Happy coding ♥
Save time and energy with our Python Code Generator. Why start from scratch when you can generate? Give it a try!
View Full Code Auto-Generate My Code



Got a coding query or need some guidance before you comment? Check out this Python Code Assistant for expert advice and handy tips. It's like having a coding tutor right in your fingertips!