Step up your coding game with AI-powered Code Explainer. Get insights like never before!
Introduction
Credit card validation is a crucial task in various financial and e-commerce applications. One of the most common algorithms used for this purpose is the Luhn algorithm. In this tutorial, I will cover how to validate a credit card number using the Luhn algorithm, detect the card type, and handle multiple card numbers from a file using Python.
Luhn Algorithm
The Luhn algorithm, also known as the "modulus 10" or "mod 10" algorithm, is a simple checksum formula used to validate various identification numbers. It is designed to protect against accidental errors, such as a single digit being mistyped or some digits being transposed.
Steps of the Luhn Algorithm:
- From the rightmost digit (the check digit), moving left, double the value of every second digit.
- If doubling of a number results in a number greater than 9, then add the digits of the product (e.g., 8 * 2 = 16 -> 1 + 6 = 7).
- Sum all the digits.
- If the total modulo 10 equals 0, then the number is valid according to the Luhn formula; otherwise, it is not valid.
Example Credit Card Number: 5555 5555 5555 4444 (Mastercard's actual test number)
- Double Every Second Digit from the Right:
- Start from the rightmost digit and double every second digit:
- 4 -> 4
- 4 -> 4 * 2 = 8
- 4 -> 4
- 4 -> 4 * 2 = 8
- 5 -> 5
- 5 -> 5 * 2 = 10 (since it's greater than 9, add the digits: 1 + 0 = 1)
- 5 -> 5
- 5 -> 5 * 2 = 10 (1 + 0 = 1)
- 5 -> 5
- 5 -> 5 * 2 = 10 (1 + 0 = 1)
- 5 -> 5
- 5 -> 5 * 2 = 10 (1 + 0 = 1)
- 5 -> 5
- 5 -> 5 * 2 = 10 (1 + 0 = 1)
- 5 -> 5
- 5 -> 5 * 2 = 10 (1 + 0 = 1)
- Start from the rightmost digit and double every second digit:
- Sum All the Digits:
- Digits: 4, 8, 4, 8, 5, 1, 5, 1, 5, 1, 5, 1, 5, 1, 5, 1
- Sum: 4 + 8 + 4 + 8 + 5 + 1 + 5 + 1 + 5 + 1 + 5 + 1 + 5 + 1 + 5 + 1 = 60
- Check if the Total Modulo 10 is 0:
- Total: 60
- 60 % 10 = 0
Since the total modulo 10 is 0, the credit card number 5555 5555 5555 4444 is valid according to the Luhn algorithm.
Implementing using Python
We'll be making use of Python 3. No need to install any package, as the ones we'll be using come pre-installed with Python. Open up a Python file, name it meaningfully, like credit_card_validation.py and follow along:
import argparse # Import argparse for command-line argument parsing
import re # Import re for regular expression matching
# Validate credit card number using Luhn Algorithm
def luhn_algorithm(card_number):
def digits_of(n):
return [int(d) for d in str(n)] # Convert each character in the number to an integer
digits = digits_of(card_number) # Get all digits of the card number
odd_digits = digits[-1::-2] # Get digits from the right, skipping one digit each time (odd positions)
even_digits = digits[-2::-2] # Get every second digit from the right (even positions)
checksum = sum(odd_digits) # Sum all odd position digits
for d in even_digits:
checksum += sum(digits_of(d*2)) # Double each even position digit and sum the resulting digits
return checksum % 10 == 0 # Return True if checksum modulo 10 is 0We started by importing re for using regular expressions (we'll use them to determine what kind of card it is) and argparse for getting user arguments from the command line. Then, we created a function to implement Luhn's algorithm.
Next, we'll create two functions. One is for checking a credit card number using the Luhn algorithm (from the function above), and the other is to get the credit card type based on the number:
# Function to get the card type based on card number using RegEx
def get_card_type(card_number):
card_number = card_number.replace(' ', '') # Remove spaces from the card number
card_types = {
"Visa": r"^4[0-9]{12}(?:[0-9]{3})?$", # Visa: Starts with 4, length 13 or 16
"MasterCard": r"^5[1-5][0-9]{14}$", # MasterCard: Starts with 51-55, length 16
"American Express": r"^3[47][0-9]{13}$", # AmEx: Starts with 34 or 37, length 15
"Discover": r"^6(?:011|5[0-9]{2})[0-9]{12}$", # Discover: Starts with 6011 or 65, length 16
"JCB": r"^(?:2131|1800|35\d{3})\d{11}$", # JCB: Starts with 2131, 1800, or 35, length 15 or 16
"Diners Club": r"^3(?:0[0-5]|[68][0-9])[0-9]{11}$", # Diners Club: Starts with 300-305, 36, or 38, length 14
"Maestro": r"^(5018|5020|5038|56|57|58|6304|6759|676[1-3])\d{8,15}$", # Maestro: Various starting patterns, length 12-19
"Verve": r"^(506[01]|507[89]|6500)\d{12,15}$" # Verve: Starts with 5060, 5061, 5078, 5079, or 6500, length 16-19
}
for card_type, pattern in card_types.items():
if re.match(pattern, card_number): # Check if card number matches the pattern
return card_type
return "Unknown" # Return Unknown if no pattern matches
The card_types dictionary in the get_card_type() function defines regular expressions (regex patterns) to identify different credit card types based on their starting digits and length:
- Visa: Matches numbers starting with a 4, having a length of 13 or 16 digits.
- MasterCard: Matches numbers starting with 51 to 55, having a length of 16 digits.
- American Express (AmEx): Matches numbers starting with 34 or 37, having a length of 15 digits.
- Discover: Matches numbers starting with 6011 or 65, having a length of 16 digits.
- JCB: Matches numbers starting with 2131, 1800, or 35 followed by three digits, having a length of 15 or 16 digits.
- Diners Club: Matches numbers starting with 300-305, 36, or 38, having a length of 14 digits.
- Maestro: Matches numbers starting with various patterns like 5018, 5020, 5038, 56, 57, 58, 6304, 6759, or 6761-6763, having a length of 12 to 19 digits.
- Verve: Matches numbers starting with 5060, 5061, 5078, 5079, or 6500, having a length of 16 to 19 digits.
Each regex pattern is designed to match specific starting sequences and digit lengths unique to each card type.
Note: I haven't tested all the card types. I used GPT-4o to get the formats of each card type and did the regular expressions for them. But for the three I've tested, they're very correct. I am telling you this in case you encounter an issue (which I doubt). The idea is just to know the pattern of a particular card type, and integrate using regular expressions.
Moving on, because we want to make our program very sophisticated, we'll add functionality to accept a text file (optionally) containing credit card numbers instead of typing them one after the other:
# Processing a file containing card numbers.
def process_file(file_path):
try:
with open(file_path, 'r') as file: # Open the file for reading
card_numbers = file.readlines() # Read all lines from the file
results = {}
for card_number in card_numbers:
card_number = card_number.strip() # Remove any leading/trailing whitespace
is_valid = check_credit_card_number(card_number) # Validate card number
card_type = get_card_type(card_number) # Detect card type
results[card_number] = (is_valid, card_type) # Store result
return results
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error reading file: {e}") # Print error message if file cannot be read
return None
Finally, we create the main function. Here, we'll use argparse to accept user arguments and handle overall program execution:
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Check if a credit card number is legitimate and identify its type using the Luhn algorithm.")
parser.add_argument('-n', '--number', type=str, help="A single credit card number to validate.") # Argument for single card number
parser.add_argument('-f', '--file', type=str, help="A file containing multiple credit card numbers to validate.") # Argument for file input
args = parser.parse_args() # Parse command-line arguments
if args.number:
is_valid = check_credit_card_number(args.number) # Validate single card number
card_type = get_card_type(args.number) # Detect card type
print(f"[!] Credit card number {args.number} is {'valid' if is_valid else 'invalid'} and is of type {card_type}.") # Print result
if args.file:
results = process_file(args.file) # Process file with card numbers
if results:
for card_number, (is_valid, card_type) in results.items():
print(f"[!] Credit card number {card_number} is {'valid' if is_valid else 'invalid'} and is of type {card_type}.") # Print results for each card number
# Execute tha main function
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The main function handles input from either a single credit card number or a file with multiple credit card numbers, validates each number using the Luhn algorithm, identifies the card type, and prints the results.
Running our Program
Let's start by running our program using just one credit card:
$ python credit_card.py -n 5555555555554444Result:
[!] Credit card number 5555555555554444 is valid and is of type MasterCard.And yes, 5555555555554444 is a Mastercard number. It is Mastercard's test number.
Screenshot:
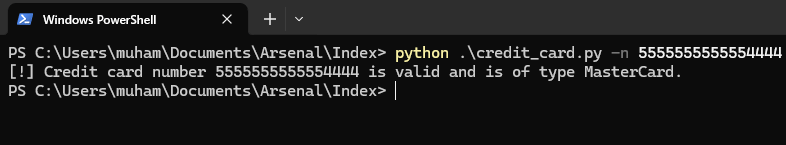
Next, we try running the program with a txt file:
python credit_card.py -f .\credit_cards.tResult:
[!] Credit card number 4111111111111111 is valid and is of type Visa.
[!] Credit card number 5555555555554444 is valid and is of type MasterCard.
[!] Credit card number 378282246310005 is valid and is of type American Express.Screenshot:
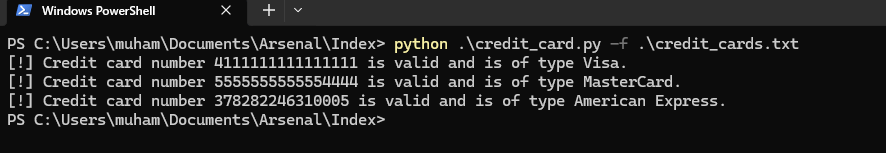
Note: These numbers are all test numbers for the various card types. Feel free to try with your own cards.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you've learned about the Luhn algorithm and how to use it to validate CC numbers and determine the card type based on patterns.
I hope you enjoyed this one, till next time! You can get the complete code here.
Related: How to Generate Fake User Data in Python
Why juggle between languages when you can convert? Check out our Code Converter. Try it out today!
View Full Code Generate Python Code


Got a coding query or need some guidance before you comment? Check out this Python Code Assistant for expert advice and handy tips. It's like having a coding tutor right in your fingertips!