Before we get started, have you tried our new Python Code Assistant? It's like having an expert coder at your fingertips. Check it out!
Being able to extract comments from the biggest video sharing website in the Internet is a handy tool, you can extract comments to perform tasks such as text classification, or you may want to extract comments of your YouTube videos to do certain tasks, the possibilities are endless.
In this tutorial, we will not only write a Python script to extract YouTube comments, but we will be experimenting with the network utility in browser's developer tools in order to capture the right comment request so that it can help us on writing the code.
Note: If the code of this tutorial doesn't work for you, please check out using YouTube API tutorial instead.
Related: How to Extract YouTube Data in Python.
Before we get started, let's install the requirements:
pip3 install requestsMonitoring Network Traffic in the Browser
Now in order to follow along with me, go into any YouTube video of your choice with Chrome or any other browser and right click and choose Inspect Element and go to Network section:
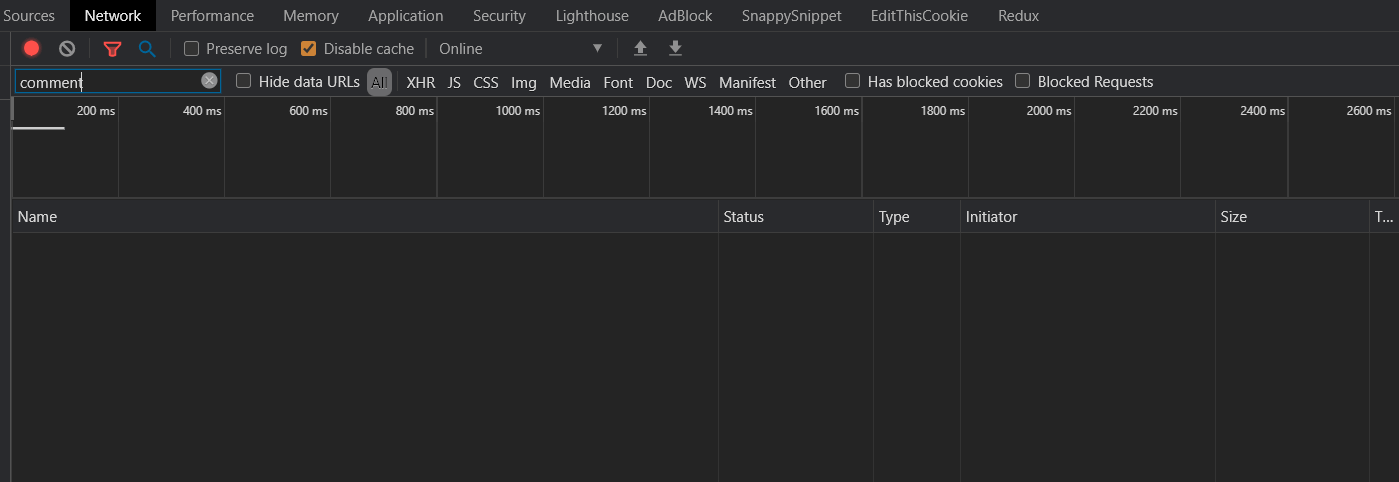
"comment" in the filter input field, this will help us filter out the unwanted HTTP requests such as images, style and Javascript files, etc.
Now go to the video page and scroll down until you see some comments loaded. If you go back to the network tool, you'll see something like this:
Great, we have successfully captured a comment request, if you click on it, you will see the actual request URL, method and the remote IP address:
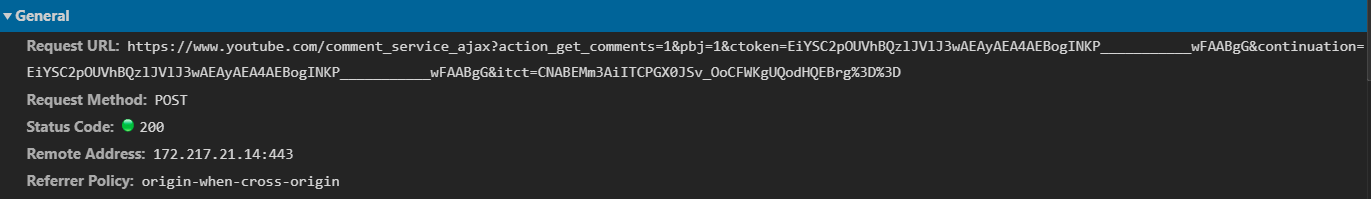
If we scroll down to the bottom in the same section (Headers), we will see the query string parameters and form data, like so:
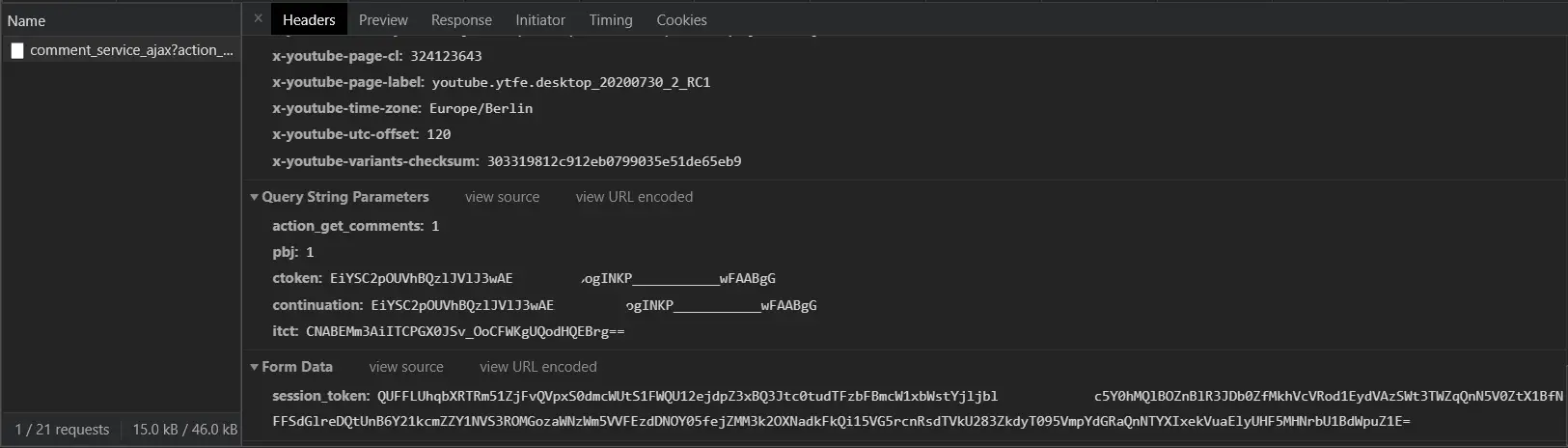
action_get_comments, pbj, ctoken, continuation, itct and session_token parameters. Notice action_get_comments and pbj parameters should have the value of 1, and ctoken and continuation have the same value. In the next section we will see how we can extract them from the YouTube video page source code using Python.
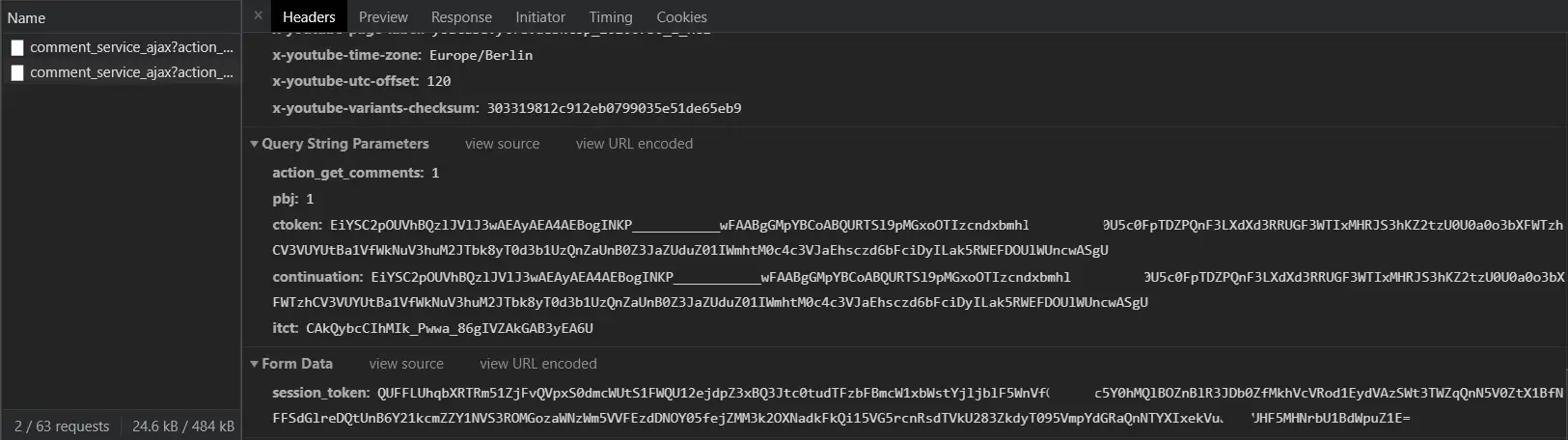
Also, if you keep scrolling down to load more comments, you'll see similar requests getting added to the requests list:
Writing the Comment Extractor in Python
Now that we understand how the comment loading request is made, let's try to simulate it in Python, importing necessary modules:
import requests
import json
import timeSince we gonna need to parse some data (the parameters seen in the last section) from the content of the video page, we won't be using HTML parser such as BeautifulSoup, that's because most of the data lives in a Javascript object within script tags. As a result, the below two functions will help us search over content:
# from https://github.com/egbertbouman/youtube-comment-downloader
def search_dict(partial, key):
"""
A handy function that searches for a specific `key` in a `partial` dictionary/list
"""
if isinstance(partial, dict):
for k, v in partial.items():
if k == key:
# found the key, return the value
yield v
else:
# value of the dict may be another dict, so we search there again
for o in search_dict(v, key):
yield o
elif isinstance(partial, list):
# if the passed data is a list
# iterate over it & search for the key at the items in the list
for i in partial:
for o in search_dict(i, key):
yield o
# from https://github.com/egbertbouman/youtube-comment-downloader
def find_value(html, key, num_sep_chars=2, separator='"'):
# define the start position by the position of the key +
# length of key + separator length (usually : and ")
start_pos = html.find(key) + len(key) + num_sep_chars
# the end position is the position of the separator (such as ")
# starting from the start_pos
end_pos = html.find(separator, start_pos)
# return the content in this range
return html[start_pos:end_pos]Don't try to understand them now, they will help us during the tokens extraction. Now let's define our core function that accepts a YouTube video URL and returns comments as a list of dictionaries:
def get_comments(url):
session = requests.Session()
# make the request
res = session.get(url)res has the HTTP response of the YouTube video web page, now let's get the session token from the returned HTML content:
# extract the XSRF token
xsrf_token = find_value(res.text, "XSRF_TOKEN", num_sep_chars=3)The XSRF token is the session_token that is required in the form data in the request, if you view the page source of the video page and you search for it, you'll find it there:
Great, let's continue on extracting other fields, which are
ctoken and itct.
The below line is responsible for extracting the Javascript object that has all the data we need:
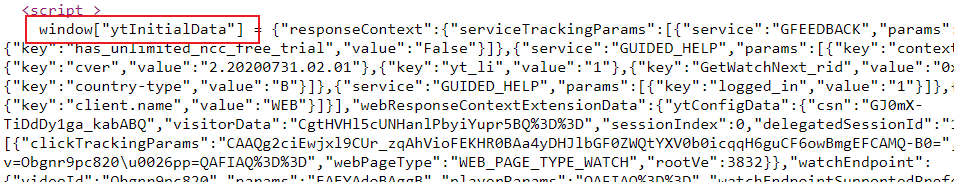
# parse the YouTube initial data in the <script> tag
data_str = find_value(res.text, 'window["ytInitialData"] = ', num_sep_chars=0, separator="\n").rstrip(";")
# convert to Python dictionary instead of plain text string
data = json.loads(data_str)Here is how it looks in page source:
Now data is a regular Python dictionary that contains all YouTube video data, now we need to search for nextContinuationData dictionary that has the required parameters:
# search for the ctoken & continuation parameter fields
for r in search_dict(data, "itemSectionRenderer"):
pagination_data = next(search_dict(r, "nextContinuationData"))
if pagination_data:
# if we got something, break out of the loop,
# we have the data we need
break
continuation_tokens = [(pagination_data['continuation'], pagination_data['clickTrackingParams'])]Going back to the page source, here is what we're searching for:
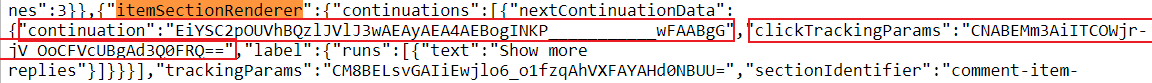 So we're interested in the
So we're interested in the continuation field (ctoken) and clickTrackingParams (itct)
The rest of the code makes a request to /comment_service_ajax to get and parse comments and gather the continuation tokens after each request we make, until there is no more comments:
while continuation_tokens:
# keep looping until continuation tokens list is empty (no more comments)
continuation, itct = continuation_tokens.pop()
# construct params parameter (the ones in the URL)
params = {
"action_get_comments": 1,
"pbj": 1,
"ctoken": continuation,
"continuation": continuation,
"itct": itct,
}
# construct POST body data, which consists of the XSRF token
data = {
"session_token": xsrf_token,
}
# construct request headers
headers = {
"x-youtube-client-name": "1",
"x-youtube-client-version": "2.20200731.02.01"
}
# make the POST request to get the comments data
response = session.post("https://www.youtube.com/comment_service_ajax", params=params, data=data, headers=headers)
# convert to a Python dictionary
comments_data = json.loads(response.text)
for comment in search_dict(comments_data, "commentRenderer"):
# iterate over loaded comments and yield useful info
yield {
"commentId": comment["commentId"],
"text": ''.join([c['text'] for c in comment['contentText']['runs']]),
"time": comment['publishedTimeText']['runs'][0]['text'],
"isLiked": comment["isLiked"],
"likeCount": comment["likeCount"],
# "replyCount": comment["replyCount"],
'author': comment.get('authorText', {}).get('simpleText', ''),
'channel': comment['authorEndpoint']['browseEndpoint']['browseId'],
'votes': comment.get('voteCount', {}).get('simpleText', '0'),
'photo': comment['authorThumbnail']['thumbnails'][-1]['url'],
"authorIsChannelOwner": comment["authorIsChannelOwner"],
}
# load continuation tokens for next comments (ctoken & itct)
continuation_tokens = [(next_cdata['continuation'], next_cdata['clickTrackingParams'])
for next_cdata in search_dict(comments_data, 'nextContinuationData')] + continuation_tokens
# avoid heavy loads with popular videos
time.sleep(0.1)Perfect, let's test this out:
if __name__ == "__main__":
from pprint import pprint
url = "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jNQXAC9IVRw"
for count, comment in enumerate(get_comments(url)):
if count == 3:
break
pprint(comment)
print("="*50)This will extract the first 3 comments and print them out:
{'author': 'wizard yt',
'authorIsChannelOwner': False,
'channel': 'UCNg8yS4kYFvvkOQFIwR5NqA',
'commentId': 'UgwiWPPBdLMwnBSCPwJ4AaABAg',
'isLiked': False,
'likeCount': 0,
'photo': 'https://yt3.ggpht.com/a/AATXAJyyoOqaBjwEGRqKzuykxNosYd76Tmj-AFUcgAzB=s48-c-k-c0xffffffff-no-rj-mo',
'text': 'Sub2sub pls i request you i want 50 subs',
'time': '2 seconds ago',
'votes': '0'}
==================================================
{'author': 'Abdou Rockikz',
'authorIsChannelOwner': False,
'channel': 'UCA4FBhVyVNMO5LcRfJKwrEA',
'commentId': 'UgzzD6ngnIFkLX_lnsx4AaABAg',
'isLiked': False,
'likeCount': 0,
'photo': 'https://yt3.ggpht.com/a/AATXAJxXbUQXU551ZKsiQ2t_DF-4yLmvG-YrDnmArCuNZw=s48-c-k-c0xffffffff-no-rj-mo',
'text': 'This is a fake comment',
'time': '4 seconds ago',
'votes': '0'}
==================================================
{'author': 'NIGHT Devil',
'authorIsChannelOwner': False,
'channel': 'UCA4FBhVyVNMO5LcRfJKwrEA',
'commentId': 'UgxbTzFsW9wrD8qvuxJ4AaABAg',
'isLiked': False,
'likeCount': 0,
'photo': 'https://yt3.ggpht.com/a/AATXAJxXbUQXU551ZKsiQ2t_DF-4yLmvG-YrDnmArCuNZw=s48-c-k-c0xffffffff-no-rj-mo',
'text': 'CLICK <hidden> for a video',
'time': '6 seconds ago',
'votes': '0'}Finally, let's use argparse module to convert this to a command line tool that is usable by anyone:
if __name__ == "__main__":
import argparse
import os
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Simple YouTube Comment extractor")
parser.add_argument("url", help="The YouTube video full URL")
parser.add_argument("-l", "--limit", type=int, help="Number of maximum comments to extract, helpful for longer videos")
parser.add_argument("-o", "--output", help="Output JSON file, e.g data.json")
# parse passed arguments
args = parser.parse_args()
limit = args.limit
output = args.output
url = args.url
from pprint import pprint
for count, comment in enumerate(get_comments(url)):
if limit and count >= limit:
# break out of the loop when we exceed limit specified
break
if output:
# write comment as JSON to a file
with open(output, "a") as f:
# begin writing, adding an opening brackets
if count == 0:
f.write("[")
f.write(json.dumps(comment, ensure_ascii=False) + ",")
else:
pprint(comment)
print("="*50)
print("total comments extracted:", count)
if output:
# remove the last comma ','
with open(output, "rb+") as f:
f.seek(-1, os.SEEK_END)
f.truncate()
# add "]" to close the list in the end of the file
with open(output, "a") as f:
print("]", file=f)This is a command line tool that accepts the YouTube video URL as required parameter, -l or --limit to limit the number of comments to extract and -o or --output to specify the output file in which the comments will be written as JSON, here is an example run:
$ python youtube_comment_extractor.py https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jNQXAC9IVRw --limit 50 --output comments50.jsonThis will extract 50 comments from that video and write them to comments50.json file.
Note: If the code of this tutorial doesn't work for you, please check out using YouTube API tutorial instead.
Conclusion
By completing this tutorial, you're able to make a simple YouTube comment extractor script. Just to note though, a part of the code for this tutorial was brought from this repository.
if you want to download much more comments, I invite you to make a progress bar manually or using tqdm library, good luck doing that!
Check out the full code here.
Learn also: How to Extract YouTube Data in Python.
Happy Scraping ♥
Just finished the article? Now, boost your next project with our Python Code Generator. Discover a faster, smarter way to code.
View Full Code Fix My Code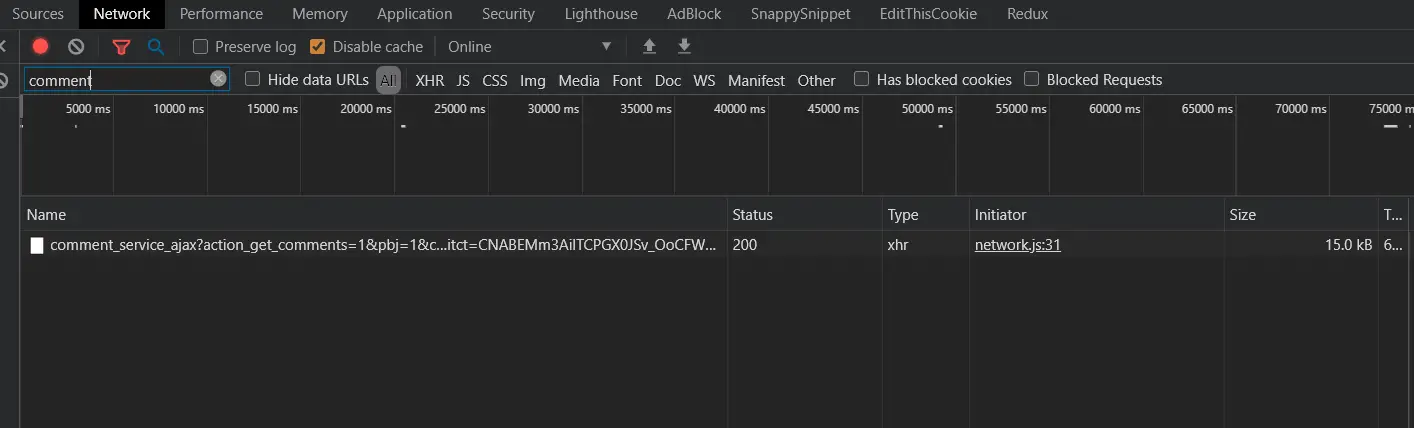


Got a coding query or need some guidance before you comment? Check out this Python Code Assistant for expert advice and handy tips. It's like having a coding tutor right in your fingertips!