Struggling with multiple programming languages? No worries. Our Code Converter has got you covered. Give it a go!
Nowadays, companies of mid and large scale have massive amounts of printed documents in daily use. Among them are invoices, receipts, corporate documents, reports, and media releases.
For those companies, the use of an OCR scanner can save a considerable amount of time while improving efficiency as well as accuracy.
Optical character recognition (OCR) algorithms allow computers to analyze printed or handwritten documents automatically and prepare text data into editable formats for computers to efficiently process them. OCR systems transform a two-dimensional image of text that could contain machine-printed or handwritten text from its image representation into machine-readable text.
Download: Practical Python PDF Processing EBook.
Generally, an OCR engine involves multiple steps required to train a machine learning algorithm for efficient problem-solving with the help of optical character recognition.
The following steps which may differ from one engine to another are roughly needed to approach automatic character recognition: Within this tutorial, I am going to show you the following:
Within this tutorial, I am going to show you the following:
- How to run an OCR scanner on an image file.
- How to redact or highlight a specific text in an image file.
- How to run an OCR scanner on a PDF file or a collection of PDF files.
Please note that this tutorial is about extracting text from images within PDF documents, if you want to extract all text from PDFs, check this tutorial instead.
To get started, we need to use the following libraries:
Tesseract OCR: is an open-source text recognition engine that is available under the Apache 2.0 license and its development has been sponsored by Google since 2006. In the year 2006, Tesseract was considered one of the most accurate open-source OCR engines. You can use it directly or can use the API to extract the printed text from images. The best part is that it supports an extensive variety of languages.
Installing the Tesseract engine is outside the scope of this article. However, you need to follow the official installation guide of Tesseract to install it on your operating system.
To validate Tesseract setup, please run the following command and check the generated output:
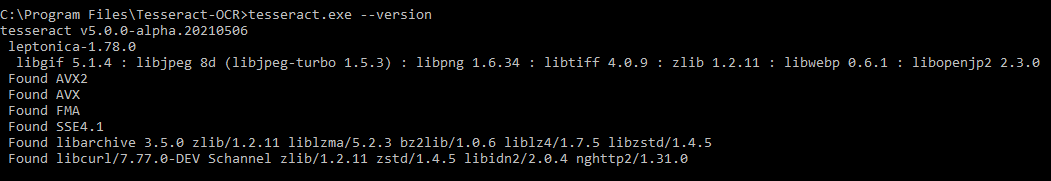 Python-tesseract: is a Python wrapper for Google’s Tesseract-OCR Engine. It is also useful as a stand-alone invocation script to tesseract, as it can read all image types supported by the Pillow and Leptonica imaging libraries, including jpeg, png, gif, bmp, tiff, and others.
Python-tesseract: is a Python wrapper for Google’s Tesseract-OCR Engine. It is also useful as a stand-alone invocation script to tesseract, as it can read all image types supported by the Pillow and Leptonica imaging libraries, including jpeg, png, gif, bmp, tiff, and others.
OpenCV: is a Python open-source library, for computer vision, machine learning, and image processing. OpenCV supports a wide variety of programming languages like Python, C++, Java, etc. It can process images and videos to identify objects, faces, or even the handwriting of a human.
PyMuPDF: MuPDF is a highly versatile, customizable PDF, XPS, and eBook interpreter solution that can be used across a wide range of applications as a PDF renderer, viewer, or toolkit. PyMuPDF is a Python binding for MuPDF. It is a lightweight PDF and XPS viewer.
Numpy: is a general-purpose array-processing package. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. It is the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python. Besides, Numpy can also be used as an efficient multi-dimensional container of generic data.
Pillow: is built on top of PIL (Python Image Library). It is an essential module for image processing in Python.
Pandas: is an open-source, BSD-licensed Python library providing high-performance, easy-to-use data structures and data analysis tools for the Python programming language.
Filetype: Small and dependency-free Python package to deduce file type and MIME type.
This tutorial aims to develop a lightweight command-line-based utility to extract, redact or highlight a text included within an image or a scanned PDF file, or within a folder containing a collection of PDF files.
Setup
To get started, let's install the requirements:
$ pip install Filetype==1.0.7 numpy==1.19.4 opencv-python==4.4.0.46 pandas==1.1.4 Pillow==8.0.1 PyMuPDF==1.18.9 pytesseract==0.3.7
Let's start by importing the necessary libraries:
import os
import re
import argparse
import pytesseract
from pytesseract import Output
import cv2
import numpy as np
import fitz
from io import BytesIO
from PIL import Image
import pandas as pd
import filetype
# Path Of The Tesseract OCR engine
TESSERACT_PATH = "C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR\tesseract.exe"
# Include tesseract executable
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = TESSERACT_PATHTESSERACT_PATH is where the Tesseract executable is located. Obviously, you need to change it for your case.
def pix2np(pix):
"""
Converts a pixmap buffer into a numpy array
"""
# pix.samples = sequence of bytes of the image pixels like RGBA
#pix.h = height in pixels
#pix.w = width in pixels
# pix.n = number of components per pixel (depends on the colorspace and alpha)
im = np.frombuffer(pix.samples, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(
pix.h, pix.w, pix.n)
try:
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im[..., [2, 1, 0]]) # RGB To BGR
except IndexError:
# Convert Gray to RGB
im = cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im[..., [2, 1, 0]]) # RGB To BGR
return imThis function converts a pixmap buffer representing a screenshot taken using the PyMuPDF library into a NumPy array.
To improve Tesseract accuracy, let's define some preprocessing functions using OpenCV:
# Image Pre-Processing Functions to improve output accurracy
# Convert to grayscale
def grayscale(img):
return cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Remove noise
def remove_noise(img):
return cv2.medianBlur(img, 5)
# Thresholding
def threshold(img):
# return cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
return cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
# dilation
def dilate(img):
kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)
return cv2.dilate(img, kernel, iterations=1)
# erosion
def erode(img):
kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)
return cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations=1)
# opening -- erosion followed by a dilation
def opening(img):
kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)
return cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
# canny edge detection
def canny(img):
return cv2.Canny(img, 100, 200)
# skew correction
def deskew(img):
coords = np.column_stack(np.where(img > 0))
angle = cv2.minAreaRect(coords)[-1]
if angle < -45:
angle = -(90 + angle)
else:
angle = -angle
(h, w) = img.shape[:2]
center = (w//2, h//2)
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0)
rotated = cv2.warpAffine(
img, M, (w, h), flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC, borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE)
return rotated
# template matching
def match_template(img, template):
return cv2.matchTemplate(img, template, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
def convert_img2bin(img):
"""
Pre-processes the image and generates a binary output
"""
# Convert the image into a grayscale image
output_img = grayscale(img)
# Invert the grayscale image by flipping pixel values.
# All pixels that are grater than 0 are set to 0 and all pixels that are = to 0 are set to 255
output_img = cv2.bitwise_not(output_img)
# Converting image to binary by Thresholding in order to show a clear separation between white and blacl pixels.
output_img = threshold(output_img)
return output_imgWe have defined functions for many preprocessing tasks, including converting images to grayscale, flipping pixel values, separating white and black pixels, and much more.
Next, let's define a function to display an image:
def display_img(title, img):
"""Displays an image on screen and maintains the output until the user presses a key"""
cv2.namedWindow('img', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.setWindowTitle('img', title)
cv2.resizeWindow('img', 1200, 900)
# Display Image on screen
cv2.imshow('img', img)
# Mantain output until user presses a key
cv2.waitKey(0)
# Destroy windows when user presses a key
cv2.destroyAllWindows()The display_img() function displays on-screen an image in a window having a title set to the title parameter and maintains this window open until the user presses a key on the keyboard.
def generate_ss_text(ss_details):
"""Loops through the captured text of an image and arranges this text line by line.
This function depends on the image layout."""
# Arrange the captured text after scanning the page
parse_text = []
word_list = []
last_word = ''
# Loop through the captured text of the entire page
for word in ss_details['text']:
# If the word captured is not empty
if word != '':
# Add it to the line word list
word_list.append(word)
last_word = word
if (last_word != '' and word == '') or (word == ss_details['text'][-1]):
parse_text.append(word_list)
word_list = []
return parse_textThe above function iterates throughout the captured text of an image and arranges the grabbed text line by line. It depends on the image layout and may require tweaking for some image formats.
Related: How to Merge PDF Files in Python.
Next, let's define a function to search for text using regular expressions:
def search_for_text(ss_details, search_str):
"""Search for the search string within the image content"""
# Find all matches within one page
results = re.findall(search_str, ss_details['text'], re.IGNORECASE)
# In case multiple matches within one page
for result in results:
yield resultWe will be using this function for searching specific text within the grabbed content of an image. It returns a generator of the found matches.
def save_page_content(pdfContent, page_id, page_data):
"""Appends the content of a scanned page, line by line, to a pandas DataFrame."""
if page_data:
for idx, line in enumerate(page_data, 1):
line = ' '.join(line)
pdfContent = pdfContent.append(
{'page': page_id, 'line_id': idx, 'line': line}, ignore_index=True
)
return pdfContentsave_page_content() function appends the grabbed content of an image line by line after scanning it to the pdfContent pandas dataframe.
Now let's make a function to save the resulting dataframe into a CSV file:
def save_file_content(pdfContent, input_file):
"""Outputs the content of the pandas DataFrame to a CSV file having the same path as the input_file
but with different extension (.csv)"""
content_file = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(input_file), os.path.splitext(
os.path.basename(input_file))[0] + ".csv")
pdfContent.to_csv(content_file, sep=',', index=False)
return content_fileNext, let's write a function that calculates the confidence score of the text grabbed from the scanned image:
def calculate_ss_confidence(ss_details: dict):
"""Calculate the confidence score of the text grabbed from the scanned image."""
# page_num --> Page number of the detected text or item
# block_num --> Block number of the detected text or item
# par_num --> Paragraph number of the detected text or item
# line_num --> Line number of the detected text or item
# Convert the dict to dataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(ss_details)
# Convert the field conf (confidence) to numeric
df['conf'] = pd.to_numeric(df['conf'], errors='coerce')
# Elliminate records with negative confidence
df = df[df.conf != -1]
# Calculate the mean confidence by page
conf = df.groupby(['page_num'])['conf'].mean().tolist()
return conf[0]Going to the main function: scanning the image:
def ocr_img(
img: np.array, input_file: str, search_str: str,
highlight_readable_text: bool = False, action: str = 'Highlight',
show_comparison: bool = False, generate_output: bool = True):
"""Scans an image buffer or an image file.
Pre-processes the image.
Calls the Tesseract engine with pre-defined parameters.
Calculates the confidence score of the image grabbed content.
Draws a green rectangle around readable text items having a confidence score > 30.
Searches for a specific text.
Highlight or redact found matches of the searched text.
Displays a window showing readable text fields or the highlighted or redacted text.
Generates the text content of the image.
Prints a summary to the console."""
# If image source file is inputted as a parameter
if input_file:
# Reading image using opencv
img = cv2.imread(input_file)
# Preserve a copy of this image for comparison purposes
initial_img = img.copy()
highlighted_img = img.copy()
# Convert image to binary
bin_img = convert_img2bin(img)
# Calling Tesseract
# Tesseract Configuration parameters
# oem --> OCR engine mode = 3 >> Legacy + LSTM mode only (LSTM neutral net mode works the best)
# psm --> page segmentation mode = 6 >> Assume as single uniform block of text (How a page of text can be analyzed)
config_param = r'--oem 3 --psm 6'
# Feeding image to tesseract
details = pytesseract.image_to_data(
bin_img, output_type=Output.DICT, config=config_param, lang='eng')
# The details dictionary contains the information of the input image
# such as detected text, region, position, information, height, width, confidence score.
ss_confidence = calculate_ss_confidence(details)
boxed_img = None
# Total readable items
ss_readable_items = 0
# Total matches found
ss_matches = 0
for seq in range(len(details['text'])):
# Consider only text fields with confidence score > 30 (text is readable)
if float(details['conf'][seq]) > 30.0:
ss_readable_items += 1
# Draws a green rectangle around readable text items having a confidence score > 30
if highlight_readable_text:
(x, y, w, h) = (details['left'][seq], details['top']
[seq], details['width'][seq], details['height'][seq])
boxed_img = cv2.rectangle(
img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Searches for the string
if search_str:
results = re.findall(
search_str, details['text'][seq], re.IGNORECASE)
for result in results:
ss_matches += 1
if action:
# Draw a red rectangle around the searchable text
(x, y, w, h) = (details['left'][seq], details['top']
[seq], details['width'][seq], details['height'][seq])
# Details of the rectangle
# Starting coordinate representing the top left corner of the rectangle
start_point = (x, y)
# Ending coordinate representing the botton right corner of the rectangle
end_point = (x + w, y + h)
#Color in BGR -- Blue, Green, Red
if action == "Highlight":
color = (0, 255, 255) # Yellow
elif action == "Redact":
color = (0, 0, 0) # Black
# Thickness in px (-1 will fill the entire shape)
thickness = -1
boxed_img = cv2.rectangle(
img, start_point, end_point, color, thickness)
if ss_readable_items > 0 and highlight_readable_text and not (ss_matches > 0 and action in ("Highlight", "Redact")):
highlighted_img = boxed_img.copy()
# Highlight found matches of the search string
if ss_matches > 0 and action == "Highlight":
cv2.addWeighted(boxed_img, 0.4, highlighted_img,
1 - 0.4, 0, highlighted_img)
# Redact found matches of the search string
elif ss_matches > 0 and action == "Redact":
highlighted_img = boxed_img.copy()
#cv2.addWeighted(boxed_img, 1, highlighted_img, 0, 0, highlighted_img)
# save the image
cv2.imwrite("highlighted-text-image.jpg", highlighted_img)
# Displays window showing readable text fields or the highlighted or redacted data
if show_comparison and (highlight_readable_text or action):
title = input_file if input_file else 'Compare'
conc_img = cv2.hconcat([initial_img, highlighted_img])
display_img(title, conc_img)
# Generates the text content of the image
output_data = None
if generate_output and details:
output_data = generate_ss_text(details)
# Prints a summary to the console
if input_file:
summary = {
"File": input_file, "Total readable words": ss_readable_items, "Total matches": ss_matches, "Confidence score": ss_confidence
}
# Printing Summary
print("## Summary ########################################################")
print("\n".join("{}:{}".format(i, j) for i, j in summary.items()))
print("###################################################################")
return highlighted_img, ss_readable_items, ss_matches, ss_confidence, output_data
# pass image into pytesseract module
# pytesseract is trained in many languages
#config_param = r'--oem 3 --psm 6'
#details = pytesseract.image_to_data(img,config=config_param,lang='eng')
# print(details)
# return detailsGet Our Practical Python PDF Processing EBook
Master PDF Manipulation with Python by building PDF tools from scratch. Get your copy now!
Download EBookThe above performs the following:
- Scans an image buffer or an image file.
- Pre-processes the image.
- Runs the Tesseract engine with pre-defined parameters.
- Calculates the confidence score of the grabbed content of the image.
- Draws a green rectangle around the readable text items having a confidence score greater than 30.
- Searches for a specific text within the image grabbed content.
- Highlights or redacts the found matches of the searched text.
- Displays a window showing readable text fields or the highlighted text or the redacted text.
- Generates the text content of the image.
- Prints a summary to the console.
def image_to_byte_array(image: Image):
"""
Converts an image into a byte array
"""
imgByteArr = BytesIO()
image.save(imgByteArr, format=image.format if image.format else 'JPEG')
imgByteArr = imgByteArr.getvalue()
return imgByteArr
def ocr_file(**kwargs):
"""Opens the input PDF File.
Opens a memory buffer for storing the output PDF file.
Creates a DataFrame for storing pages statistics
Iterates throughout the chosen pages of the input PDF file
Grabs a screen-shot of the selected PDF page.
Converts the screen-shot pix to a numpy array
Scans the grabbed screen-shot.
Collects the statistics of the screen-shot(page).
Saves the content of the screen-shot(page).
Adds the updated screen-shot (Highlighted, Redacted) to the output file.
Saves the whole content of the PDF file.
Saves the output PDF file if required.
Prints a summary to the console."""
input_file = kwargs.get('input_file')
output_file = kwargs.get('output_file')
search_str = kwargs.get('search_str')
pages = kwargs.get('pages')
highlight_readable_text = kwargs.get('highlight_readable_text')
action = kwargs.get('action')
show_comparison = kwargs.get('show_comparison')
generate_output = kwargs.get('generate_output')
# Opens the input PDF file
pdfIn = fitz.open(input_file)
# Opens a memory buffer for storing the output PDF file.
pdfOut = fitz.open()
# Creates an empty DataFrame for storing pages statistics
dfResult = pd.DataFrame(
columns=['page', 'page_readable_items', 'page_matches', 'page_total_confidence'])
# Creates an empty DataFrame for storing file content
if generate_output:
pdfContent = pd.DataFrame(columns=['page', 'line_id', 'line'])
# Iterate throughout the pages of the input file
for pg in range(pdfIn.pageCount):
if str(pages) != str(None):
if str(pg) not in str(pages):
continue
# Select a page
page = pdfIn[pg]
# Rotation angle
rotate = int(0)
# PDF Page is converted into a whole picture 1056*816 and then for each picture a screenshot is taken.
# zoom = 1.33333333 -----> Image size = 1056*816
# zoom = 2 ---> 2 * Default Resolution (text is clear, image text is hard to read) = filesize small / Image size = 1584*1224
# zoom = 4 ---> 4 * Default Resolution (text is clear, image text is barely readable) = filesize large
# zoom = 8 ---> 8 * Default Resolution (text is clear, image text is readable) = filesize large
zoom_x = 2
zoom_y = 2
# The zoom factor is equal to 2 in order to make text clear
# Pre-rotate is to rotate if needed.
mat = fitz.Matrix(zoom_x, zoom_y).preRotate(rotate)
# To captue a specific part of the PDF page
# rect = page.rect #page size
# mp = rect.tl + (rect.bl - (0.75)/zoom_x) #rectangular area 56 = 75/1.3333
# clip = fitz.Rect(mp,rect.br) #The area to capture
# pix = page.getPixmap(matrix=mat, alpha=False,clip=clip)
# Get a screen-shot of the PDF page
# Colorspace -> represents the color space of the pixmap (csRGB, csGRAY, csCMYK)
# alpha -> Transparancy indicator
pix = page.getPixmap(matrix=mat, alpha=False, colorspace="csGRAY")
# convert the screen-shot pix to numpy array
img = pix2np(pix)
# Erode image to omit or thin the boundaries of the bright area of the image
# We apply Erosion on binary images.
#kernel = np.ones((2,2) , np.uint8)
#img = cv2.erode(img,kernel,iterations=1)
upd_np_array, pg_readable_items, pg_matches, pg_total_confidence, pg_output_data \
= ocr_img(img=img, input_file=None, search_str=search_str, highlight_readable_text=highlight_readable_text # False
, action=action # 'Redact'
, show_comparison=show_comparison # True
, generate_output=generate_output # False
)
# Collects the statistics of the page
dfResult = dfResult.append({'page': (pg+1), 'page_readable_items': pg_readable_items,
'page_matches': pg_matches, 'page_total_confidence': pg_total_confidence}, ignore_index=True)
if generate_output:
pdfContent = save_page_content(
pdfContent=pdfContent, page_id=(pg+1), page_data=pg_output_data)
# Convert the numpy array to image object with mode = RGB
#upd_img = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(upd_np_array)).convert('RGB')
upd_img = Image.fromarray(upd_np_array[..., ::-1])
# Convert the image to byte array
upd_array = image_to_byte_array(upd_img)
# Get Page Size
"""
#To check whether initial page is portrait or landscape
if page.rect.width > page.rect.height:
fmt = fitz.PaperRect("a4-1")
else:
fmt = fitz.PaperRect("a4")
#pno = -1 -> Insert after last page
pageo = pdfOut.newPage(pno = -1, width = fmt.width, height = fmt.height)
"""
pageo = pdfOut.newPage(
pno=-1, width=page.rect.width, height=page.rect.height)
pageo.insertImage(page.rect, stream=upd_array)
#pageo.insertImage(page.rect, stream=upd_img.tobytes())
#pageo.showPDFpage(pageo.rect, pdfDoc, page.number)
content_file = None
if generate_output:
content_file = save_file_content(
pdfContent=pdfContent, input_file=input_file)
summary = {
"File": input_file, "Total pages": pdfIn.pageCount,
"Processed pages": dfResult['page'].count(), "Total readable words": dfResult['page_readable_items'].sum(),
"Total matches": dfResult['page_matches'].sum(), "Confidence score": dfResult['page_total_confidence'].mean(),
"Output file": output_file, "Content file": content_file
}
# Printing Summary
print("## Summary ########################################################")
print("\n".join("{}:{}".format(i, j) for i, j in summary.items()))
print("\nPages Statistics:")
print(dfResult, sep='\n')
print("###################################################################")
pdfIn.close()
if output_file:
pdfOut.save(output_file)
pdfOut.close()The image_to_byte_array() function converts an image into a byte array.
The ocr_file() function does the following:
- Opens the input PDF file.
- Opens a memory buffer for storing the output PDF file.
- Creates a pandas dataframe for storing the page's statistics.
- Iterates through the chosen pages of the input PDF file.
- Grabs a screenshot (image) of the selected page of the input PDF file.
- Converts the screenshot (pix) to a NumPy array.
- Scans the grabbed screen-shot.
- Collects the statistics of the screen-shot (page).
- Saves the content of the screenshot.
- Adds the updated screenshot to the output file.
- Saves the whole content of the input PDF file to a CSV file.
- Saves the output PDF file if required.
- Prints a summary to the console.
Let's add another function for processing a folder that contains multiple PDF files:
def ocr_folder(**kwargs):
"""Scans all PDF Files within a specified path"""
input_folder = kwargs.get('input_folder')
# Run in recursive mode
recursive = kwargs.get('recursive')
search_str = kwargs.get('search_str')
pages = kwargs.get('pages')
action = kwargs.get('action')
generate_output = kwargs.get('generate_output')
# Loop though the files within the input folder.
for foldername, dirs, filenames in os.walk(input_folder):
for filename in filenames:
# Check if pdf file
if not filename.endswith('.pdf'):
continue
# PDF File found
inp_pdf_file = os.path.join(foldername, filename)
print("Processing file =", inp_pdf_file)
output_file = None
if search_str:
# Generate an output file
output_file = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(
inp_pdf_file), 'ocr_' + os.path.basename(inp_pdf_file))
ocr_file(
input_file=inp_pdf_file, output_file=output_file, search_str=search_str, pages=pages, highlight_readable_text=False, action=action, show_comparison=False, generate_output=generate_output
)
if not recursive:
breakThis function is intended to scan the PDF files included within a specific folder. It loops throughout the files of the specified folder either recursively or not depending on the value of the parameter recursive and processes these files one by one.
It accepts the following parameters:
input_folder: The path of the folder containing the PDF files to process.search_str: The text to search for to manipulate.recursive: whether to run this process recursively by looping across the subfolders or not.action: the action to perform among the following: Highlight, Redact.pages: the pages to consider.generate_output: select whether to save the content of the input PDF file to a CSV file or not
Before we finish, let's define useful functions for parsing command-line arguments:
def is_valid_path(path):
"""Validates the path inputted and checks whether it is a file path or a folder path"""
if not path:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid Path")
if os.path.isfile(path):
return path
elif os.path.isdir(path):
return path
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid Path {path}")
def parse_args():
"""Get user command line parameters"""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Available Options")
parser.add_argument('-i', '--input-path', type=is_valid_path,
required=True, help="Enter the path of the file or the folder to process")
parser.add_argument('-a', '--action', choices=[
'Highlight', 'Redact'], type=str, help="Choose to highlight or to redact")
parser.add_argument('-s', '--search-str', dest='search_str',
type=str, help="Enter a valid search string")
parser.add_argument('-p', '--pages', dest='pages', type=tuple,
help="Enter the pages to consider in the PDF file, e.g. (0,1)")
parser.add_argument("-g", "--generate-output", action="store_true", help="Generate text content in a CSV file")
path = parser.parse_known_args()[0].input_path
if os.path.isfile(path):
parser.add_argument('-o', '--output_file', dest='output_file',
type=str, help="Enter a valid output file")
parser.add_argument("-t", "--highlight-readable-text", action="store_true", help="Highlight readable text in the generated image")
parser.add_argument("-c", "--show-comparison", action="store_true", help="Show comparison between captured image and the generated image")
if os.path.isdir(path):
parser.add_argument("-r", "--recursive", action="store_true", help="Whether to process the directory recursively")
# To Porse The Command Line Arguments
args = vars(parser.parse_args())
# To Display The Command Line Arguments
print("## Command Arguments #################################################")
print("\n".join("{}:{}".format(i, j) for i, j in args.items()))
print("######################################################################")
return argsThe is_valid_path() function validates a path inputted as a parameter and checks whether it is a file path or a directory path.
The parse_args() function defines and sets the appropriate constraints for the user's command-line arguments when running this utility.
Below are explanations for all the parameters:
input_path: A required parameter to input the path of the file or the folder to process, this parameter is associated with theis_valid_path()function previously defined.action: The action to perform among a list of pre-defined options to avoid any erroneous selection.search_str: The text to search for to manipulate.pages: the pages to consider when processing a PDF file.generate_content: specifies whether to generate the input file's grabbed content, whether an image or a PDF to a CSV file or not.output_file: The path of the output file. Filling in this argument is constrained by the selection of a file as input, not a directory.highlight_readable_text: to draw green rectangles around readable text fields having a confidence score greater than 30.show_comparison: Displays a window showing a comparison between the original image and the processed image.recursive: whether to process a folder recursively or not. Filling in this argument is constrained by the selection of a directory.
Finally, let's write the main code that uses previously defined functions:
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Parsing command line arguments entered by user
args = parse_args()
# If File Path
if os.path.isfile(args['input_path']):
# Process a file
if filetype.is_image(args['input_path']):
ocr_img(
# if 'search_str' in (args.keys()) else None
img=None, input_file=args['input_path'], search_str=args['search_str'], highlight_readable_text=args['highlight_readable_text'], action=args['action'], show_comparison=args['show_comparison'], generate_output=args['generate_output']
)
else:
ocr_file(
input_file=args['input_path'], output_file=args['output_file'], search_str=args['search_str'] if 'search_str' in (args.keys()) else None, pages=args['pages'], highlight_readable_text=args['highlight_readable_text'], action=args['action'], show_comparison=args['show_comparison'], generate_output=args['generate_output']
)
# If Folder Path
elif os.path.isdir(args['input_path']):
# Process a folder
ocr_folder(
input_folder=args['input_path'], recursive=args['recursive'], search_str=args['search_str'] if 'search_str' in (args.keys()) else None, pages=args['pages'], action=args['action'], generate_output=args['generate_output']
)Get Our Practical Python PDF Processing EBook
Master PDF Manipulation with Python by building PDF tools from scratch. Get your copy now!
Download EBookLet's test our program:
$ python pdf_ocr.pyOutput:
usage: pdf_ocr.py [-h] -i INPUT_PATH [-a {Highlight,Redact}] [-s SEARCH_STR] [-p PAGES] [-g GENERATE_OUTPUT]
Available Options
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT_PATH, --input_path INPUT_PATH
Enter the path of the file or the folder to process
-a {Highlight,Redact}, --action {Highlight,Redact}
Choose to highlight or to redact
-s SEARCH_STR, --search_str SEARCH_STR
Enter a valid search string
-p PAGES, --pages PAGES
Enter the pages to consider e.g.: (0,1)
-g GENERATE_OUTPUT, --generate_output GENERATE_OUTPUT
Generate content in a CSV fileBefore exploring our test scenarios, beware of the following:
- To avoid encountering the
PermissionErrorerror, please close the input file before running this utility. - The search string complies with the rules of regular expressions using Python's built-in re module. For example, setting the search string to "organi[sz]e" matches both "organise" and "organize".
First, let's try to input an image (you can get it here if you want to get the same output), without any PDF file involved:
$ python pdf_ocr.py -s "BERT" -a Highlight -i example-image-containing-text.jpgThe following will be the output:
## Command Arguments #################################################
input_path:example-image-containing-text.jpg
action:Highlight
search_str:BERT
pages:None
generate_output:False
output_file:None
highlight_readable_text:False
show_comparison:False
######################################################################
## Summary ########################################################
File:example-image-containing-text.jpg
Total readable words:192
Total matches:3
Confidence score:89.89337547979804
###################################################################And a new image has appeared in the current directory:
 You can pass
You can pass -t or --highlight-readable-text to highlight all detected text (with a different format, so as to distinguish the searching string from the others).
You can also pass -c or --show-comparison to display the original image and the edited image in the same window.
Now that's working for images, let's try for PDF files:
$ python pdf_ocr.py -s "BERT" -i image.pdf -o output.pdf --generate-output -a "Highlight"image.pdf is a simple PDF file containing the image in the previous example (again, you can get it here).
This time we've passed a PDF file to the -i argument, and output.pdf as the resulting PDF file (where all the highlighting occurs). The above command generates the following output:
## Command Arguments #################################################
input_path:image.pdf
action:Highlight
search_str:BERT
pages:None
generate_output:True
output_file:output.pdf
highlight_readable_text:False
show_comparison:False
######################################################################
## Summary ########################################################
File:image.pdf
Total pages:1
Processed pages:1
Total readable words:192.0
Total matches:3.0
Confidence score:83.1775128855722
Output file:output.pdf
Content file:image.csv
Pages Statistics:
page page_readable_items page_matches page_total_confidence
0 1.0 192.0 3.0 83.177513
###################################################################The output.pdf file is produced after the execution, where it includes the same original PDF but with highlighted text. Additionally, we have now statistics about our PDF file, where 192 total words have been detected, and 3 were matched using our search with a confidence of about 83.2%.
A CSV file is also generated that includes the detected text from the image on each line.
Get Our Practical Python PDF Processing EBook
Master PDF Manipulation with Python by building PDF tools from scratch. Get your copy now!
Download EBookConclusion
There are other parameters we didn't use in our examples, feel free to explore them. You can also pass an entire folder to the -i argument to scan a collection of PDF files.
Tesseract is perfect for scanning clean and clear documents. A poor-quality scan may produce poor results in OCR. Normally, it doesn’t give accurate results of the images affected by artifacts including partial occlusion, distorted perspective, and complex background.
Get the full code here.
Here are some other related PDF tutorials:
- How to Watermark PDF Files in Python.
- How to Highlight and Redact Text in PDF Files with Python.
- How to Extract Images from PDF in Python.
- How to Extract All PDF Links in Python.
- How to Extract Tables from PDF in Python.
- How to Sign PDF Files in Python.
- How to Extract PDF Metadata in Python.
Finally, for more PDF handling guides on Python, you can check our Practical Python PDF Processing EBook, where we dive deeper into PDF document manipulation with Python, make sure to check it out here if you're interested!
Happy coding ♥
Want to code smarter? Our Python Code Assistant is waiting to help you. Try it now!
View Full Code Auto-Generate My Code


Got a coding query or need some guidance before you comment? Check out this Python Code Assistant for expert advice and handy tips. It's like having a coding tutor right in your fingertips!