Ready to take Python coding to a new level? Explore our Python Code Generator. The perfect tool to get your code up and running in no time. Start now!
Compressing PDF allows you to decrease the file size as small as possible while maintaining the quality of the media in that PDF file. As a result, it significantly increases effectiveness and shareability.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to compress PDF files using the PDFTron library in Python.
PDFNetPython3 is a wrapper for PDFTron SDK. With PDFTron components, you can build reliable & speedy applications that can view, create, print, edit, and annotate PDFs across various operating systems. Developers use PDFTron SDK to read, write, and edit PDF documents compatible with all published versions of PDF specifications (including the latest ISO32000).
PDFTron is not freeware. It offers two licenses depending on whether you're developing an external/commercial product or an in-house solution.
We will use the free trial version of this SDK for this tutorial. This tutorial aims to develop a lightweight command-line-based utility through Python-based modules without relying on external utilities outside the Python ecosystem (e.g., Ghostscript) that compress PDF files.
Note that this tutorial only works for compressing PDF files and not any file. You can check this tutorial for compressing and archiving files.
Read also: How to Compress Images in Python.
To get started, let's install the Python wrapper using pip:
$ pip install PDFNetPython3==8.1.0Open up a new Python file and import the necessary modules:
# Import Libraries
import os
import sys
from PDFNetPython3.PDFNetPython import PDFDoc, Optimizer, SDFDoc, PDFNetNext, let's define a function that prints the file size in the appropriate format (grabbed from this tutorial):
def get_size_format(b, factor=1024, suffix="B"):
"""
Scale bytes to its proper byte format
e.g:
1253656 => '1.20MB'
1253656678 => '1.17GB'
"""
for unit in ["", "K", "M", "G", "T", "P", "E", "Z"]:
if b < factor:
return f"{b:.2f}{unit}{suffix}"
b /= factor
return f"{b:.2f}Y{suffix}"Download: Practical Python PDF Processing EBook.
Now let's define our core function:
def compress_file(input_file: str, output_file: str):
"""Compress PDF file"""
if not output_file:
output_file = input_file
initial_size = os.path.getsize(input_file)
try:
# Initialize the library
PDFNet.Initialize()
doc = PDFDoc(input_file)
# Optimize PDF with the default settings
doc.InitSecurityHandler()
# Reduce PDF size by removing redundant information and compressing data streams
Optimizer.Optimize(doc)
doc.Save(output_file, SDFDoc.e_linearized)
doc.Close()
except Exception as e:
print("Error compress_file=", e)
doc.Close()
return False
compressed_size = os.path.getsize(output_file)
ratio = 1 - (compressed_size / initial_size)
summary = {
"Input File": input_file, "Initial Size": get_size_format(initial_size),
"Output File": output_file, f"Compressed Size": get_size_format(compressed_size),
"Compression Ratio": "{0:.3%}.".format(ratio)
}
# Printing Summary
print("## Summary ########################################################")
print("\n".join("{}:{}".format(i, j) for i, j in summary.items()))
print("###################################################################")
return TrueGet Our Practical Python PDF Processing EBook
Master PDF Manipulation with Python by building PDF tools from scratch. Get your copy now!
Download EBookThis function compresses a PDF file by removing redundant information and compressing the data streams; it then prints a summary showing the compression ratio and the size of the file after compression. It takes the PDF input_file and produces the compressed PDF output_file.
Now let's define our main code:
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Parsing command line arguments entered by user
input_file = sys.argv[1]
output_file = sys.argv[2]
compress_file(input_file, output_file)We get the input and output files from the command-line arguments and then use our defined compress_file() function to compress the PDF file.
Let's test it out:
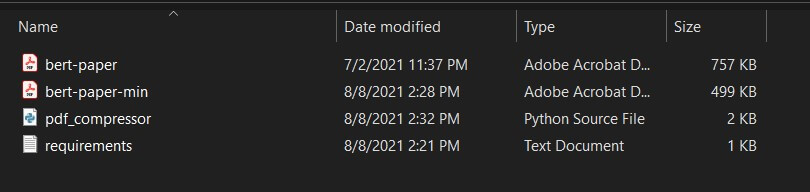
$ python pdf_compressor.py bert-paper.pdf bert-paper-min.pdfThe following is the output:
PDFNet is running in demo mode.
Permission: read
Permission: optimizer
Permission: write
## Summary ########################################################
Input File:bert-paper.pdf
Initial Size:757.00KB
Output File:bert-paper-min.pdf
Compressed Size:498.33KB
Compression Ratio:34.171%.
###################################################################As you can see, a new compressed PDF file with the size of 498KB instead of 757KB. Check this out:
 Conclusion
Conclusion
I hope you enjoyed the tutorial and found this PDF compressor helpful for your tasks.
Here are some other related PDF tutorials:
- How to Convert HTML to PDF in Python.
- How to Highlight and Redact Text in PDF Files with Python.
- How to Extract Images from PDF in Python.
- How to Extract All PDF Links in Python.
- How to Extract Tables from PDF in Python.
- How to Extract Text from Images in PDF Files with Python.
- How to Extract PDF Metadata in Python.
- How to Sign PDF Files in Python.
Check the complete code here.
Finally, unlock the secrets of Python PDF manipulation! Our compelling Practical Python PDF Processing eBook offers exclusive, in-depth guidance you won't find anywhere else. If you're passionate about enriching your skill set and mastering the intricacies of PDF handling with Python, your journey begins with a single click right here. Let's explore together!
Happy coding ♥
Loved the article? You'll love our Code Converter even more! It's your secret weapon for effortless coding. Give it a whirl!
View Full Code Improve My Code


Got a coding query or need some guidance before you comment? Check out this Python Code Assistant for expert advice and handy tips. It's like having a coding tutor right in your fingertips!